Reservoir constraints in Prodrisk#
In Prodrisk, a hydropower module can contain both minimum and maximum reservoir constraints. In the API, both of these constraints can be set in two different ways:
The attributes minVol and maxVol are given with weekly resolution. When using these constraints, the model enforces the reservoir to satisfy the given constraints at the end of the week, i.e. the last time step. For the remaining time steps within the week, the following logic is applied:
If a minvol/maxvol constraint in week \(N\) is stricter (resp. increased/decreased) than the constraint in week \(N-1\), the new constraint will only apply in the last time step in week \(N\), whereas the earlier constraint applies for the time steps before.
If a minvol/maxvol constraint in week \(N\) is looser (resp. decreased/increased) than the constraint in week \(N-1\), the new constraint will apply for all time steps in week \(N\).
In conclusion, when introducing a stricter minVol or maxVol constraint in the model, it should be set starting one week before the intended start time, such that it will be satisfied immediately in the intended period.
The attributes min_vol_hourly and max_vol_hourly are given with up to hourly resolution, but are converted to price period resolution within the Prodrisk core. The constraints will apply in the same time steps as given in the input. When these constraints are used to calculate internal values with weekly resolution in the Prodrisk core (i.e. head coefficients, buffer reservoir curves, extra cuts), the average min/max reservoir constraints within the week is used. Note that min_vol_hourly is incompatible with a soft reservoir constraint, and will be interpreted as an absolute constraint regardless of the choice of reservoirMinRestrictionType.
When running Prodrisk from the CLI, reservoir constraints are only available on weekly resolution (minVol, maxVol). The attributes min_vol_hourly and max_vol_hourly are only available through the API.
Soft reservoir constraints in Prodrisk#
For the minimum reservoir constraint minVol, two choices are available: Absolute or hard reservoir constraints, and soft reservoir constraints. This is set through the attribute reservoirMinRestrictionType. This is not the case for min_vol_hourly which is always interpreted as an absolute constraint. The intention of a soft constraint is to act as a stop discharge reservoir constraint. The minimum reservoir constraint can be motivated by e.g. public use of nature, or biodiversity.
The hard constraint is easy to understand. For each week when the constraint is active, it limits the reservoir to be within the limit given by the user. If the minimum reservoir constraint is violated, a penalty is added to the objective function.
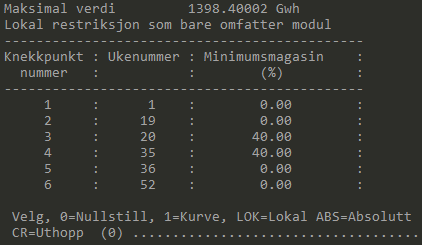
The soft constraint is slightly more sophisticated. For each week when the constraint is active, a limitation acts on the reservoir, just like for the hard constraint. However, this limitation is not the same as the user gave as input to the system. Instead, an internal, hard constraint is calculated based on the average inflow. This internal, hard constraint works just like the regular hard constraint described above, with a penalty added to the objective function if it is crossed. The user provided, soft constraint on the other hand will not be visible at all in the LP-problem.
If the option write_penalty_logfiles in prodrisk.CPAR is set to 1, the constraint will be printed out, showing both the provided soft reservoir constraint and the translated hard reservoir constraint:
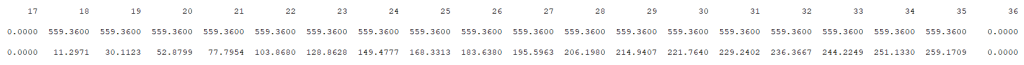
Setting soft reservoir constraints in CLI#
To set soft reservoir constriants in the command line interface, this can be done using the med.exe program for the relevant module. Selecting the choice 18 Minimalmagasin and the option LOK enables you to add weekly values for the soft reservoir constraint, as shown below: